Language function and dysfunction lab
At the Language Function and Dysfunction Lab, we study the psychology, neuropsychology, and neurobiology of language in healthy individuals and in individuals with brain damage.
Our approach is bi-directional. On the one hand, we use models from cognitive neuroscience to better understand language function in neurological populations with the goal of contributing to the development of novel diagnostic tools and methods to improve language capacity in patients. On the other hand, we use observations of the breakdown of language and communicative abilities following brain insult to obtain unique insights informative for cognitive (neuro)science models.
We have a strong focus on language production (because, of course, you can’t do it all!), but are also interested in comprehension and, especially, the intersection between production and comprehension. Most of our work is based on behavioural measures, electrophysiology, diffusion-weighted imaging, and non-invasive brain stimulation.
For teaching resources on language production, check Speaking: The free book (chapter). It’s free and at an appropriate entry level!
Looking for an internship? Contact us!
Research line
File drawer
Research line
We will be again at SNL this year (from our homes). Follow the links for more. Matteo will present his work on semantic and phonological context effects using picture-word interference and EEG.
We are excited about participating in and presenting at the International Workshop on Language Production this year (from our homes). Follow the links for more (links will be updated soon).
We are excited about attending SNL this year (from our homes). Follow the links for more. Check Joanna’s poster for exciting findings on the temporal lobe white matter in humans vs chimps.
We are very excited to present at Science of Aphasia. Click on the links to see more. We will update the pages to include more info later. Joanna will give a talk on comparative neuroanatomy of the posterior temporal lobe at the white matter level: chimps vs humans!
We will be presenting lots of interesting stuff at SNL this year. Click on the links to see more. We will update the pages to include more info later.
Source reconstruction of magnetoencephalography (MEG) has been used to assess brain reorganization after brain damage, such as stroke. Lesions result in parts of the brain having an electrical conductivity that differs from the normal values. The effect this has on the forward solutions (i.e., the propagation of electric currents and …
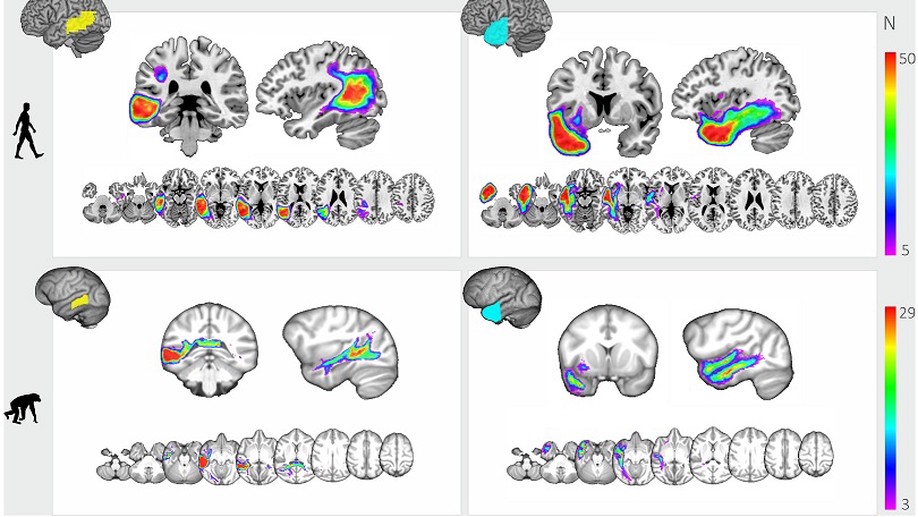
The biological foundation for the language-ready brain in the human lineage remains a debated subject. In humans, the arcuate fasciculus (AF) white matter and the posterior portions of the middle temporal gyrus are crucial for language. Compared with other primates, the human AF has been shown to dramatically extend into the …
Background: Neurocognition and speech, relevant domains in head and neck cancer (HNC), may be affected pretreatment. However, the prevalence of pretreatment deficits and their possible concurrent predictors are poorly understood. Methods: Using an HNC prospective cohort (Netherlands Quality of Life and Biomedical Cohort Study, N ≥ …
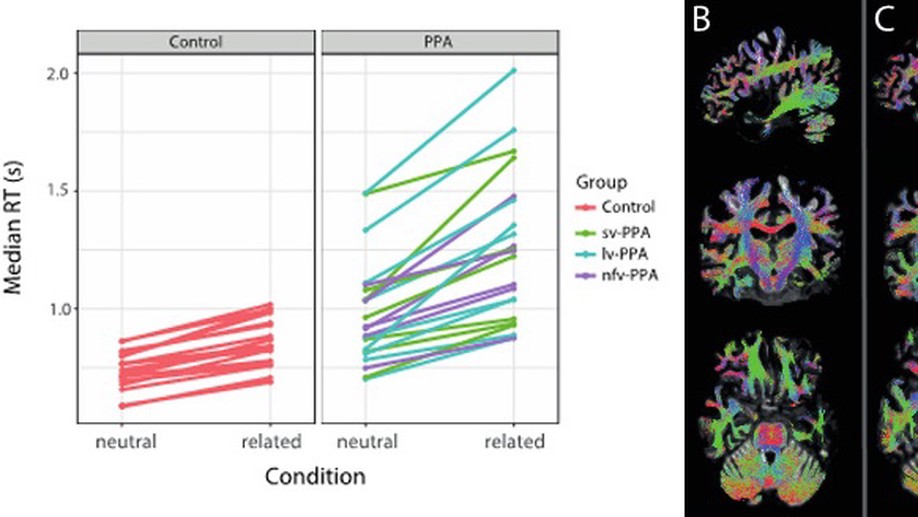
Primary progressive aphasia (PPA) is a clinical neurodegenerative syndrome with word finding problems as a core clinical symptom. Many aspects of word finding have been clarified in psycholinguistics using picture naming and a picture-word interference (PWI) paradigm, which emulates naming under contextual noise. However, little is …
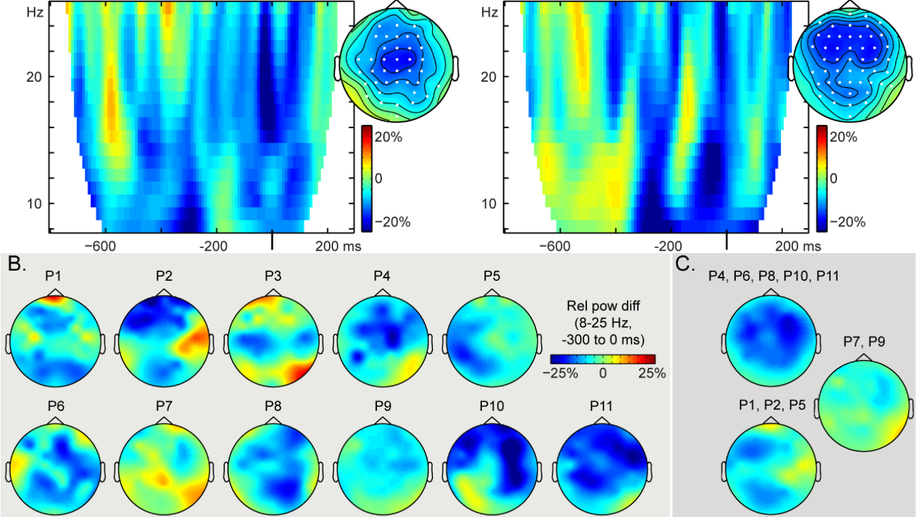
Studies suggest that alpha–beta power decreases index word retrieval in context-driven word production. We recorded the electroencephalogram from patients with stroke lesions encompassing the left lateral-temporal and inferior-parietal regions or left lateral-frontal lobe. Results indicate a critical role for the left posterior, but not frontal cortex, in generating the alpha–beta power decreases underlying context‐driven word production.
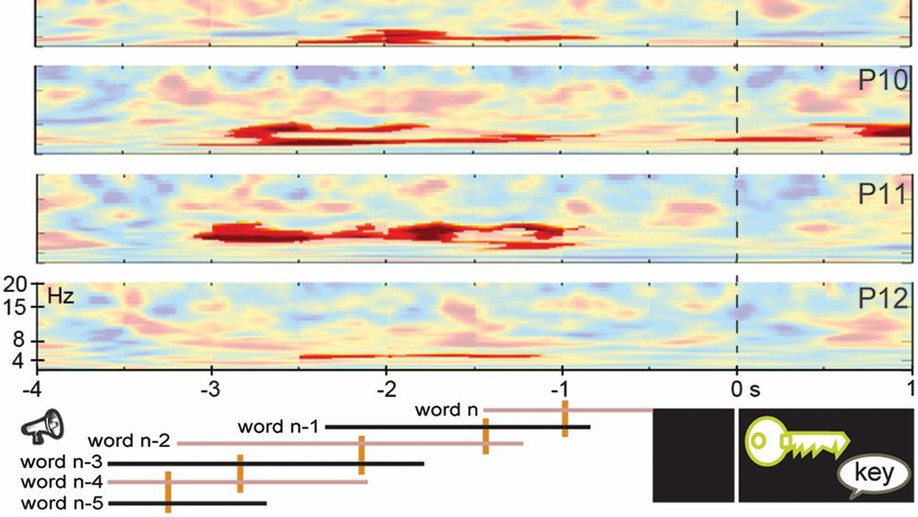
Language is typically studied in isolation from memory. We demonstrate that the same neuronal computations used by the hippocampus for memory also subserve online language usage. These findings represent a major step in integrating the studies of language and memory, significantly expanding the role of hippocampal theta oscillations.
This book was written as a resource for teaching language production at the Bachelor’s and Master’s level or for initiating trainees on the topic more generally. Some basic knowledge of cognitive psychology and linguistics is assumed. These materials only exist thanks to the help of the authors of the different sections. Sections are …
Discourse production, including the use of discourse particles, is crucial in everyday communication. Discourse particles (e.g., ja ‘yeah’) form a heterogeneous group of words that fulfil different functions such as structuring the discourse or marking the relationship between the hearer and speaker. Primary progressive …
There is ongoing debate about the role of ventral anterior temporal lobe (vATL) regions in the initial stages of production, particularly in accessing conceptual knowledge, with most evidence coming from visual naming tasks. Here, we investigated whether these regions are engaged during naming from different types of auditory …
It has been proposed that a decline in memory strategy use underlies part of the age-related decline in associative memory. Particularly internal strategies, which are very beneficial for memorization, tend to be used less as people age. We examined the relationship between age and self-initiated internal memory strategies and tested …
Goal-directed behavior requires adjusting cognitive control, both in preparation for and in reaction to conflict. Theta oscillations and population activity in dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (dmPFC) and dorsolateral PFC (dlPFC) are known to support reactive control. Here, we investigated their role in proactive control using human …